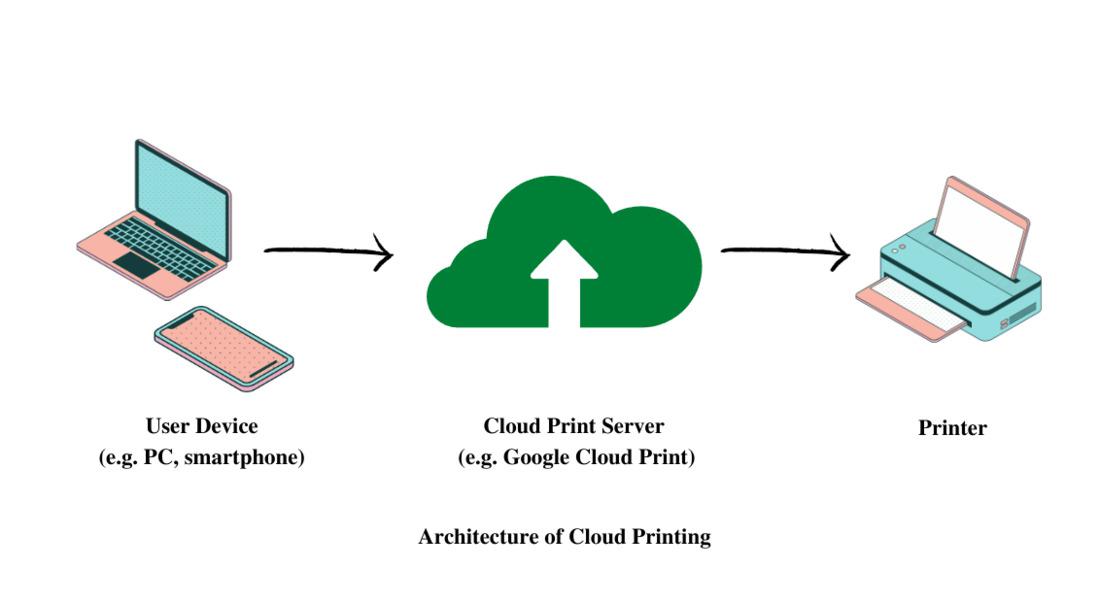
Introduction
In today’s hybrid and mobile-first work environments, the traditional model of printing — sitting at a desktop, connected directly to a local printer via USB or local network — is showing its age. Enter cloud printing: a modern solution that lets users send print jobs from anywhere, from any device, to a printer connected via the internet.
In this article we’ll explore: what cloud printing is, how it works, its key components, the benefits and challenges, and how you might adopt it in your organization or home setup.
What Is Cloud Printing?
Cloud printing refers to a technology that enables users to submit print jobs to a printer via the internet, rather than being physically connected or tied to a local network and specific drivers.
In practical terms: you could be on a smartphone, tablet or laptop — even offsite or travelling — and you can send a document to be printed at a designated printer in an office, printing service or remote location.
There are different scenarios of cloud printing:
Commercial/production cloud print services: where digital content is printed “on demand” across distributed facilities via cloud infrastructure.
Consumer-based cloud printing: printing from mobile devices or PCs to a home or public printer.
Corporate / enterprise cloud printing: enabling employees to print from anywhere to any printer managed by the company, often without print servers on-site.

How Does Cloud Printing Work?
To understand cloud printing, let’s break down the flow and key components.
1. Initiating the Print Job
A user on a device (laptop, smartphone, tablet) selects a document or file and chooses to print. Instead of the document being sent to a locally connected printer via USB or local driver, the job is sent to a cloud print service.
Often this involves uploading the document, or sending a job to a cloud-based queue.
2. Cloud Processing & Authentication
The cloud print service authenticates the user (ensuring correct permissions, user identity) and converts the print job into a format the destination printer can handle. The service may also manage driver-less printing, or cloud-ready printers.
The job may be temporarily stored (encrypted) in the cloud until printing is triggered.
3. Routing to the Printer
Once the job is ready, the cloud service routes it to the target printer. This printer could be “cloud-ready” (internet-connected on its own) or “legacy” (on-premises but accessible via a connector).
The printer receives the job, converts it to physical output, and prints the document. The print server or service keeps track of the queue and job status.
4. Feedback & Monitoring
Most cloud printing solutions provide status updates: e.g., job completed, error occurred, device offline, etc. Administrators can track usage, quotas, security events and printing behaviour centrally.

Key Components of Cloud Printing
To make sense of the architecture, here are the major components:
Security & Authentication Layer: Ensures only authorized users/devices can print, and that the transmissions are encrypted.
User Device: Laptop, desktop, smartphone, tablet — anywhere the user starts the print job.
Cloud Print Service / Server: Hosts the printing workflow, authenticates user, formats job, queues it, and routes it.
Print Queue / Driver / Format Converter: Converts the document into a printable format and manages job sequencing.
Printer (Cloud-Ready or Legacy): The destination device that actually prints the job. Legacy printers may need a “cloud connector”.
Network / Internet Connectivity: Because communication happens over the cloud/internet, devices and printers need connectivity and appropriate access.
Why Use Cloud Printing? The Benefits
Cloud printing offers several compelling advantages, especially in modern business and hybrid work environments:
Flexibility & Mobility
You can send print jobs from anywhere: home, coffee shop, on the road — to a printer in the office or another location. No need to be physically plugged in.
Reduced Infrastructure & Cost Savings
By moving print management to the cloud, organizations can reduce dependence on on-premises print servers, reduce maintenance, energy usage, and physical space.
Simplified Driver & Device Management
With cloud printing, the need for installing specific drivers or managing printer configuration on each device is minimized or eliminated. Users can print whatever device they use.
Centralised Control & Monitoring
IT teams can monitor usage, enforce print policies, track print jobs, manage quotas, and gain analytics — all from one interface.
Support for Hybrid/Remote Work
As more workers operate remotely or in hybrid modes, cloud printing allows them to still print to office printers or designated print points — bridging the digital-physical gap.
Enhanced Security Options
Many cloud printing architectures now support encryption in transit and at rest, strong authentication and “pull-print” (where the job is only released when user authenticates at the printer).
Future Trends in Cloud Printing
The world of printing is evolving. Here are a few trends worth watching:
Improved Security & Zero Trust Models: As print jobs often contain sensitive data, cloud print architectures are adopting zero-trust security frameworks, end-to-end encryption and stronger authentication.
Zero-driver Printing & Universal Print Platforms: Solutions that remove the need for drivers entirely and integrate with identity management platforms (e.g., via Microsoft Universal Print) for seamless printing.
Hybrid & Edge Print Architectures: Combining cloud management with local print processing for performance and latency optimisation.
Print Analytics & Sustainability: Cloud print services increasingly offer analytics on usage, cost, wastage and integrate with green-printing initiatives.
Integration with IoT & Smart Devices: Printers themselves becoming smarter, connected, able to be managed and provisioned via IoT.
Conclusion
As workplaces become more fluid, mobile and distributed, the way we print must evolve. Traditional print infrastructures — tethered to local networks, physical drivers and desktop PCs — simply don’t fit the new normal. Cloud printing offers a modern alternative: a printing model built for the internet era.